In the diagram which one represents a hypertonic solution? This question delves into the fascinating realm of osmosis and cellular behavior, where understanding the concept of hypertonic solutions is paramount. Hypertonic solutions, characterized by a higher solute concentration compared to another solution, play a crucial role in various biological processes and have significant implications in fields ranging from medicine to agriculture.
As we explore the characteristics and effects of hypertonic solutions, we will uncover the secrets hidden within diagrams, enabling us to accurately identify these solutions and comprehend their impact on living cells.
Hypertonic Solutions
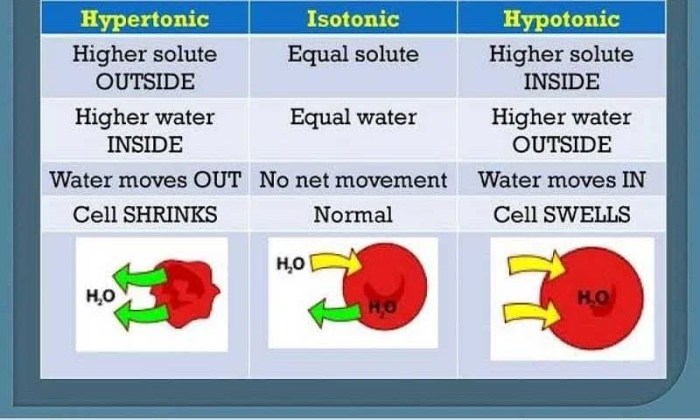
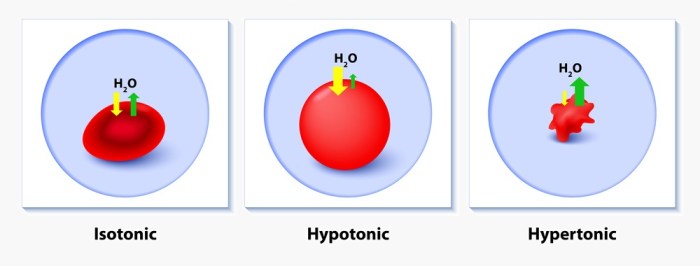
A hypertonic solution is a solution with a higher concentration of solutes than another solution, causing water to move out of the latter and into the former through osmosis.
Identify Hypertonic Solution in a Diagram
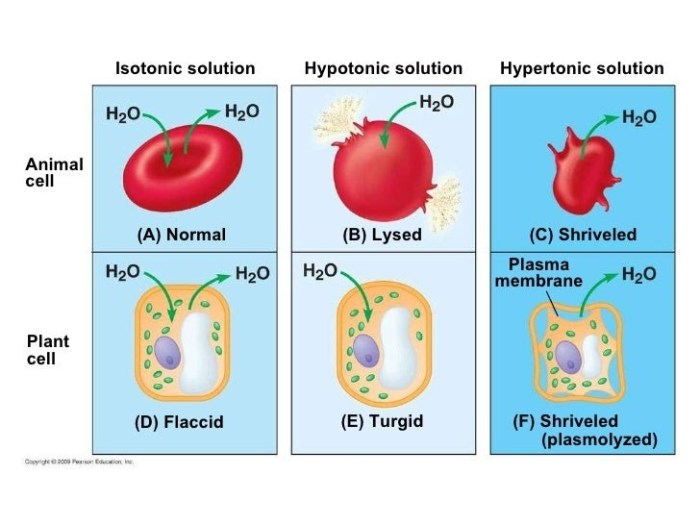
In a diagram, a hypertonic solution is represented by a cell that is smaller and shrunken compared to a cell in an isotonic solution. The cell membrane of the cell in the hypertonic solution is also pulled away from the cell wall.
Effects of Hypertonic Solution on Cells
Animal Cells
- Water moves out of the cell, causing it to shrink.
- The cell membrane may detach from the cell wall.
- The cell may become crenated, or indented.
Plant Cells
- Water moves out of the cell, causing it to lose turgor pressure.
- The cell membrane detaches from the cell wall, and the cell becomes plasmolyzed.
- The cell may eventually die.
Importance of Hypertonic Solutions
Hypertonic solutions are used in a variety of fields, including:
- Medicine: To treat dehydration and electrolyte imbalances.
- Food preservation: To prevent the growth of bacteria.
- Industry: To remove water from products, such as in the production of cheese and paper.
Additional Examples and Applications, In the diagram which one represents a hypertonic solution
| Solution | Concentration | Application | Explanation |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sodium chloride | 0.9% | Intravenous fluids | To treat dehydration and electrolyte imbalances |
| Sucrose | 50% | Food preservation | To prevent the growth of bacteria |
| Calcium chloride | 25% | Road deicing | To lower the freezing point of water |
FAQ Guide: In The Diagram Which One Represents A Hypertonic Solution
What is the key characteristic of a hypertonic solution?
A hypertonic solution has a higher solute concentration compared to another solution.
How can I identify a hypertonic solution in a diagram?
Look for a solution with a higher concentration of solute particles represented by dots or circles.
What is the effect of a hypertonic solution on animal cells?
Animal cells placed in a hypertonic solution will shrink due to water loss through osmosis.