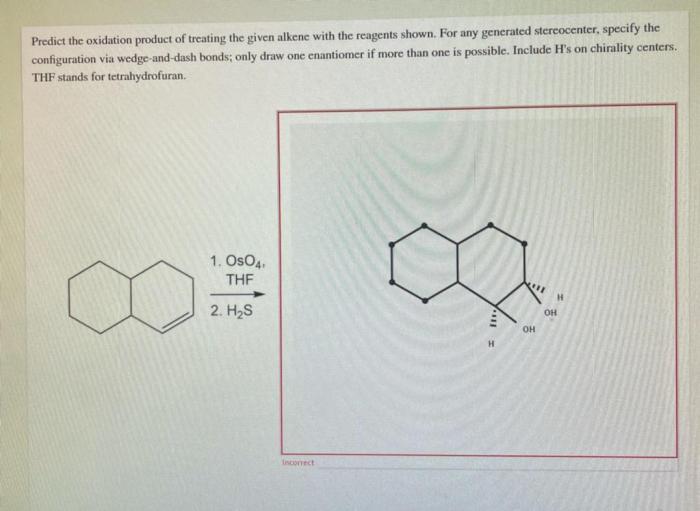
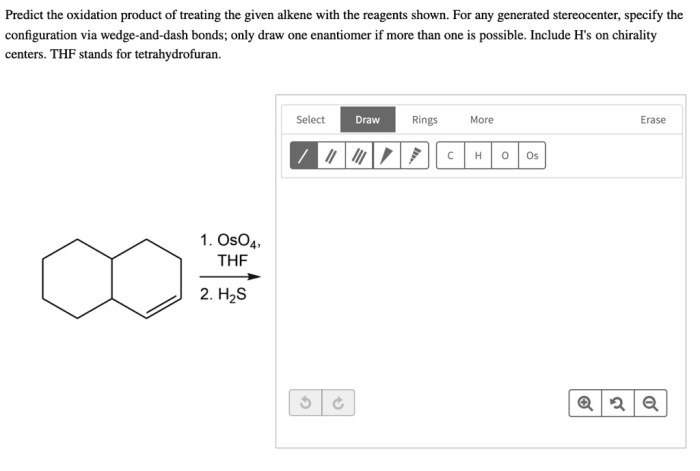
Predict the oxidation product of treating the given alkeneis a fundamental concept in organic chemistry that involves understanding the mechanisms, regioselectivity, and stereoselectivity of alkene oxidation reactions. This process plays a vital role in various fields, including pharmaceuticals, fragrances, and polymers.
Oxidation reactions of alkenes can yield a variety of products, including epoxides, diols, and aldehydes/ketones. The choice of oxidizing agent, reaction conditions, and alkene structure can influence the outcome of these reactions.
Predict the Oxidation Product of Treating the Given Alkene
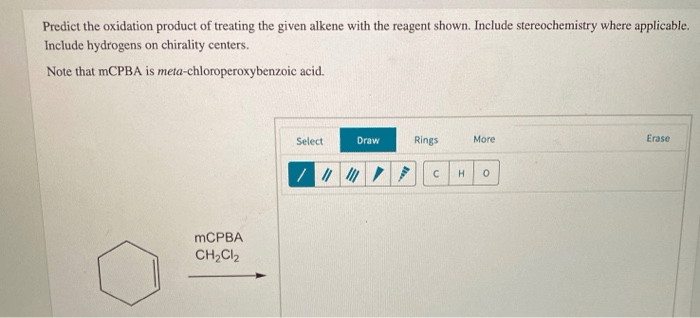
Alkene oxidation is a versatile reaction that can be used to produce a variety of functional groups. The regio- and stereoselectivity of the reaction can be controlled by the choice of oxidizing agent and reaction conditions.
Oxidation Mechanisms
Alkenes can be oxidized by a variety of oxidizing agents, including potassium permanganate, ozone, and peroxyacids. The mechanism of the reaction depends on the oxidizing agent used.
Potassium permanganate is a strong oxidizing agent that can oxidize alkenes to diols. The reaction proceeds via a cyclic intermediate, which is formed by the addition of permanganate to the double bond. The intermediate then collapses to form a diol.
Ozone is a less reactive oxidizing agent than potassium permanganate. It can oxidize alkenes to epoxides or diols, depending on the reaction conditions. The reaction proceeds via a concerted mechanism, in which the ozone molecule adds to the double bond to form an ozonide intermediate.
The intermediate then collapses to form an epoxide or a diol.
Peroxyacids are weak oxidizing agents that can oxidize alkenes to epoxides. The reaction proceeds via a concerted mechanism, in which the peroxyacid adds to the double bond to form an epoxide intermediate. The intermediate then collapses to form an epoxide.
Regioselectivity and Stereoselectivity
The regioselectivity of an alkene oxidation reaction is determined by the position of the double bond relative to the oxidizing agent. The stereoselectivity of the reaction is determined by the orientation of the double bond relative to the oxidizing agent.
Markownikoff’s rule states that the addition of an electrophile to an alkene will occur in a way that results in the formation of the more substituted carbocation. This rule can be used to predict the regioselectivity of alkene oxidation reactions.
There are a number of exceptions to Markownikoff’s rule. One exception is the addition of peroxyacids to alkenes. Peroxyacids add to alkenes in a way that results in the formation of the less substituted carbocation.
Reaction Conditions
The reaction conditions can have a significant effect on the outcome of an alkene oxidation reaction. The temperature, solvent, and concentration of the reactants can all affect the regioselectivity, stereoselectivity, and efficiency of the reaction.
The temperature of the reaction can affect the regioselectivity of the reaction. Higher temperatures favor the formation of the more substituted carbocation. This is because the higher temperature provides more energy for the carbocation to form.
The solvent can affect the regioselectivity and stereoselectivity of the reaction. Protic solvents favor the formation of the more substituted carbocation. This is because the protic solvent can donate a proton to the carbocation, which helps to stabilize it.
The concentration of the reactants can affect the efficiency of the reaction. Higher concentrations of the reactants favor the formation of the desired product. This is because the higher concentration of the reactants increases the probability of the reactants colliding with each other.
Applications of Alkene Oxidation, Predict the oxidation product of treating the given alkene
Alkene oxidation reactions are used in a variety of industrial and academic applications. Some of the most common applications include:
- The synthesis of pharmaceuticals
- The synthesis of fragrances
- The synthesis of polymers
Alkene oxidation reactions are a powerful tool for the synthesis of a variety of functional groups. The regio- and stereoselectivity of the reaction can be controlled by the choice of oxidizing agent and reaction conditions.
Key Questions Answered: Predict The Oxidation Product Of Treating The Given Alkene
What factors influence the regioselectivity of alkene oxidation reactions?
The regioselectivity of alkene oxidation reactions is influenced by the stability of the carbocation intermediate formed during the reaction. More stable carbocations are formed when the double bond is attacked at the less substituted carbon, leading to Markovnikov’s addition.
How does the concentration of the oxidizing agent affect the outcome of alkene oxidation reactions?
The concentration of the oxidizing agent can affect the rate and selectivity of alkene oxidation reactions. Higher concentrations of the oxidizing agent can lead to faster reactions and increased formation of over-oxidized products.