A horizontal platform in the shape of a circular disk is a geometric form that finds applications in diverse fields, ranging from engineering to architecture. Its unique shape and properties make it a versatile and structurally sound design, prompting us to delve into its characteristics, applications, and significance in this comprehensive exploration.
The circular disk’s geometric properties, including its radius, diameter, and circumference, define its shape and provide insights into its area and volume. Its structural stability stems from the inherent strength of the circular form, which can withstand various forces and stresses.
This makes circular disks suitable for load-bearing applications and structural components.
1. Definition and Overview

A horizontal platform in the shape of a circular disk is a flat, two-dimensional surface that lies parallel to the ground and has the form of a circle. It is a common geometric shape found in various applications and objects.
Examples of real-world objects that resemble this shape include the tops of tables, circular saws, and the bases of cylindrical containers.
2. Geometric Properties
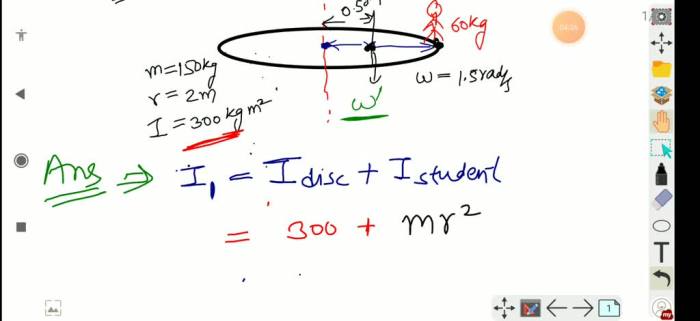
A circular disk is characterized by its radius (r), which is the distance from the center of the circle to any point on its edge, and its diameter (d), which is the length of a straight line passing through the center and connecting two points on the edge.
The circumference (C) of the disk is the distance around its edge and is calculated as C = 2πr, where π is a mathematical constant approximately equal to 3.14.
The area (A) of the disk is the amount of two-dimensional space it occupies and is given by A = πr 2.
3. Structural Analysis
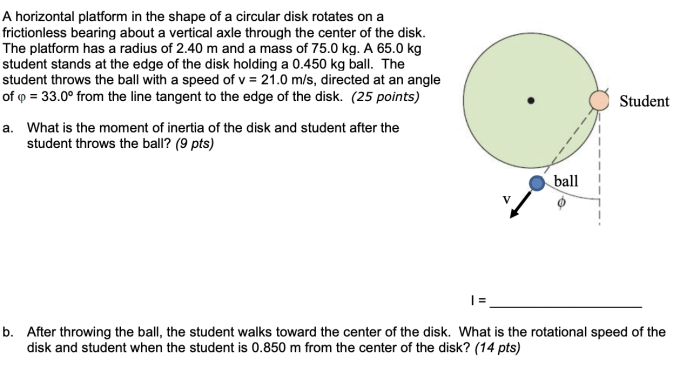
The shape of a circular disk contributes to its structural stability by evenly distributing forces and stresses around its circumference.
Factors affecting the strength and rigidity of the disk include the material properties, such as elasticity and yield strength, as well as its thickness.
4. Applications and Design Considerations
Circular disks are commonly used in industries and applications such as engineering, manufacturing, and architecture.
When designing circular disks, engineers consider factors such as load-bearing capacity, material selection, and manufacturing processes.
5. Historical and Cultural Significance: A Horizontal Platform In The Shape Of A Circular Disk
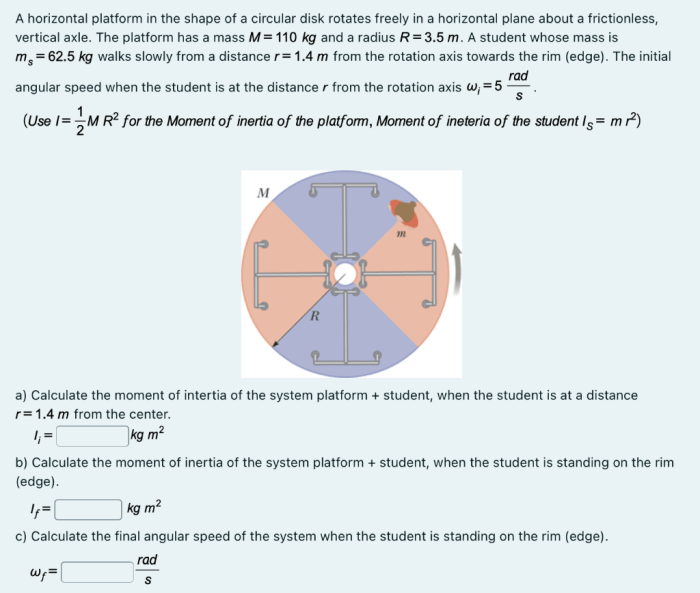
Circular disks have historical significance dating back to ancient times, with examples found in architectural structures, such as columns and arches, and in cultural symbols, such as the sun and the moon.
In various societies, circular disks have played roles in art, religion, and mythology, representing concepts of unity, eternity, and celestial bodies.
Expert Answers
What is the primary advantage of using a circular disk shape?
The circular disk shape provides inherent structural stability and load-bearing capacity due to its uniform distribution of forces and stresses.
In which industries are circular disks commonly employed?
Circular disks find applications in engineering, manufacturing, architecture, and design, among others.
What factors influence the strength and rigidity of a circular disk?
The strength and rigidity of a circular disk are influenced by factors such as the material properties, thickness, and boundary conditions.